![]() THE AGE OF REVOLUTIONS 1642-1791• • THE NOTIONS
THE AGE OF REVOLUTIONS 1642-1791• • THE NOTIONS
The facts
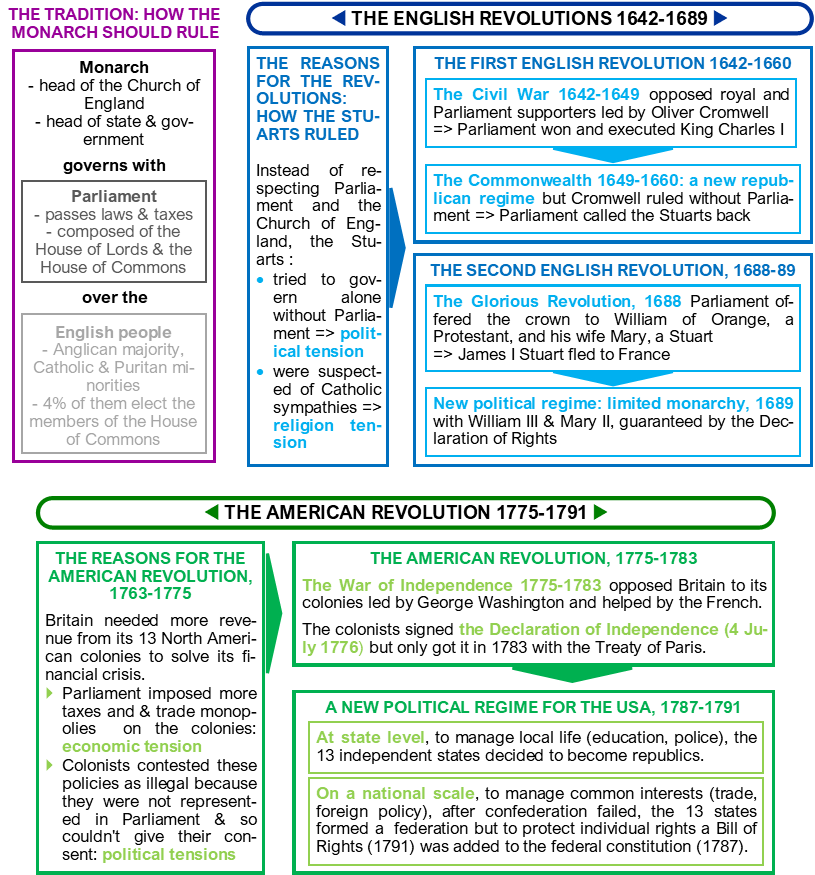
Definitions of key notions & vocabulary
Political regimes
• monarchy: a political regime in which the head of state is a hereditary monarch.
• absolute monarchy: when the monarch holds all powers and makes all decisions.
• arbitrary power: when people in power make decisions without justifying them, so viewed as unfair by the people.
• tyranny: when people in government abuse their power and oppress the people, don’t respect their rights.
• parliamentary monarchy: when royal power is limited, controlled by the people represented in a parliament; the monarch is not above the law but must obey it.
• republic: a political regime in which the head of state is elected by the people.
• democracy: system of government based on the belief in freedom and equality, in which power is held by the people.
• confederation: a loose association of states with a weak central government.
• federation: a tight association of states with a strong central government.
Political powers
• separation of powers: each power (legislative, executive and judicial) is held by a different player (person or institution) to prevent abuse of power.
• sovereignty of the people: the nation, the people is the basis of all legitimate power.
• representation of the people: when the people take part in political decisions thanks to elected representatives.
Political crisis
• revolution: popular uprising leading to drastic political and social change ; based on the right to rebel: if a government doesn’t respect people’s rights, they are justified in overthrowing it.
• civil war: a war between different groups in one country to take control of the government or become independent.
• colony: an overseas territory controlled and governed by a foreign power.
• state: a independent, free territory with its own government.
Religious tensions
• Anglican, Anglicanism: mild form of Protestantism, predominant in England where the monarch is the head of the Church of England.
• Catholic, Catholicism: also called Roman catholic, papist, Popery by Protestants, as the Pope in Rome is the head of the Catholic Church.
Economic tensions
• fiscal policy : more revenuefor the government means the people pay more taxes.
• trade monopoly: government commercial policy which allows a company to be the only one to trade goods with its colonies.