![]() A CHANGING WORLD • • The notions
A CHANGING WORLD • • The notions
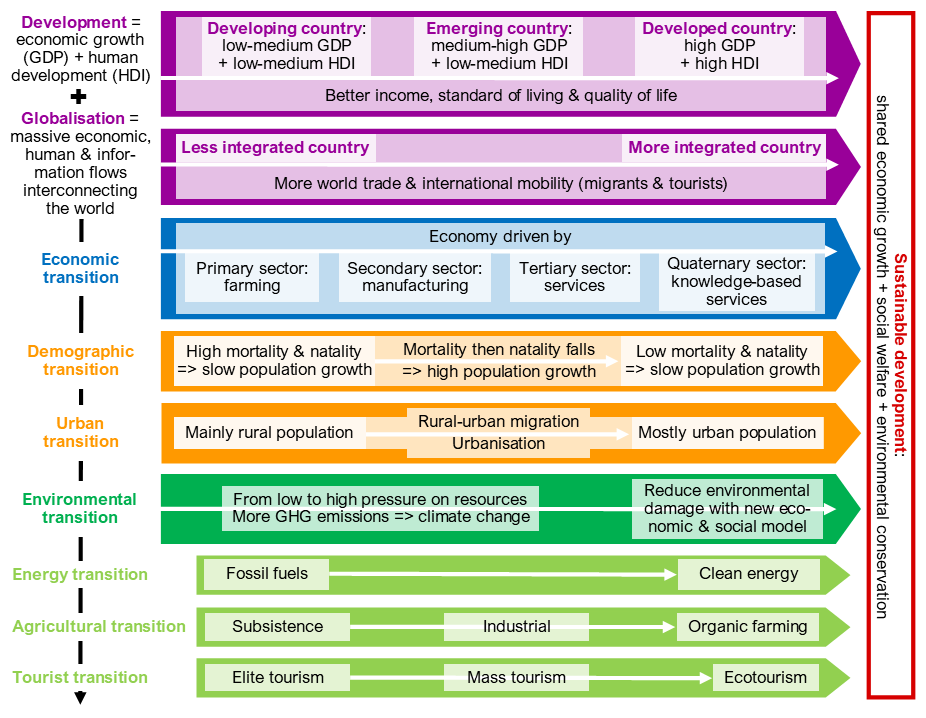
Definitions of key notions & vocabulary
Transitions
• the demographic transition: change from a high to a low natality and mortality with a population boom (high population growth).
• the urban transition: shift from a mostly rural to a mainly urban population.
• the economic transition: change from an economy driven first by farming, then by manufacturing and last by services.
• the energy transition: giving up fossil fuel and use clean, renewable energies to decarbonise activities.
• the environmental transition: reducing environmental damage with new ways of producing and consuming.
• the agricultural transition: shift from subsistence to industrial farming and then more sustainable practices like organic farming.
• the tourist transition: progress towards a more democratised and sustainable tourism.
Development
• Gross Domestic Product (GDP): measures the standard of living.
• Human Development Index (HDI): measures the quality of life.
• a developed country: with a high income (GDP) and human development (HDI).
• a developing country: with a medium or low income (GDP) and human development (HDI).
• an emerging country: a developing country with a strong economic growth but a medium HDI. The most powerful are the BRICSAM: Brazil, Russia, India, China, South Africa & Mexico.
• sustainable development: shared economic growth + social welfare + environmental protection.
• unsustainable development: economic crisis + social inequality + environmental damage.
Mobility
• globalisation: massive economic, human & information flows interconnecting the world.
• mobility: move to a new location for a visit (tourist) or to settle (migrant).
• rural-urban migration: rural population moving to cities where they live in degraded housing (slums).
• push factor: negative reason why people want to leave a place.
• pull factor: positive reason why people are attracted to a place.
• multicultural society: cosmopolitan society, with many different ethnic communities living side by side.
Environment
• climate change: extreme weather driven by global warming due to increasing greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions from human activity.
• pressure on resources: natural resources strained by damaging practices (pollution, waste or overuse).
• green or ecotourism: supporting environmental conservation, social inclusion and local economies, so sustainable.