![]() The Industrial Age 1815-1914 • • THE NOTIONS
The Industrial Age 1815-1914 • • THE NOTIONS
The facts
Definitions of key notions & vocabulary
Industrialisation
• domestic system / cottage industry: small scale hand home-made production.
• Industrial Revolution: shift from hand home-made to mass factory production.
• factory system: production on a large scale in a single centralized location.
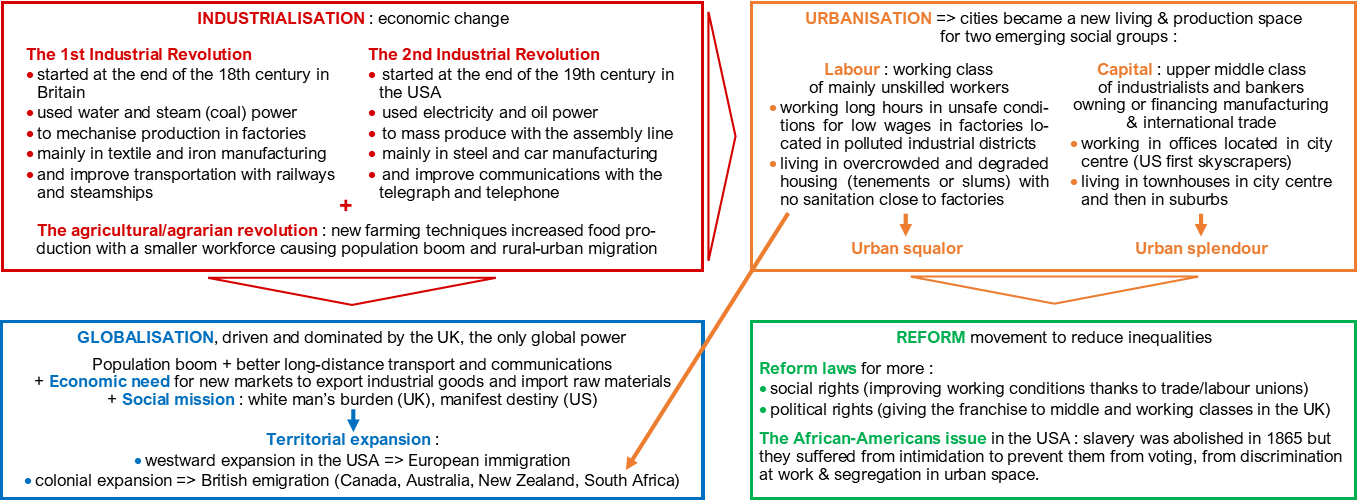
• 1st Industrial Revolution: see flow chart.
• 2nd Industrial Revolution: see flow chart.
• assembly line: assembling parts into a finished product is broken down into a series of small, simple tasks.
• industrialisation: shift from an economy based on farming to one driven by manufacturing. (2E-G economic transition)
Globalisation (def 2E-G)
• migration: movement of people from one place to settle permanently in a new location. (2E-G mobility)
• push factor: negative reason why people want to leave a place. (2E-G)
• pull factor: positive reason why people are attracted to a place. (2E-G)
• territorial expansion: see flow chart.
• colonisation: conquering & controlling colonies (def 2E-H) to form an empire.
• colonialism: doctrine aiming at justifying colonisation.
• imperialism: the will to expand a country’s power, domination over another people, territory.
• the white man’s burden (UK), manifest destiny (USA): the duty, mission of the British/Americans to bring progress to, “civilize” other people considered as inferior.
Urbanisation
• agrarian / agricultural revolution: see flow chart.
• demographic transition: shift from a high to a low mortality and natality with a population boom. (2E-G)
• rural-urban migration: inflow of rural population to cities where they lived in degraded housing. (2E-G)
• urbanisation: increasing concentration of population in cities.
• urban transition: shift from a mostly rural to a mainly urban population. (2E-G)
• Labour living in urban squalor: see flow chart.
• Capital living in urban spendour: see flow chart.
Reform
• reform movement: movement to improve social well-being or political rights by passing laws reducing abuse, inequality.
• trade union (UK), labour union (US): organization of workers who unite to protect their rights from abusive practices by their employer.
• strike: if workers refuse to work, to improve poor working conditions, low wages.
• democratisation: the transition to a more democratic political regime, to a full democracy (def in 2E-H) by, for example, extending the franchise.
• franchise: the right to vote ; can be restricted or universal -excluding or including citizens because or regardless of gender, wealth etc...