![]() GLOBAL CITIES• • The notions
GLOBAL CITIES• • The notions
Facts
Definitions of key notions & vocabulary
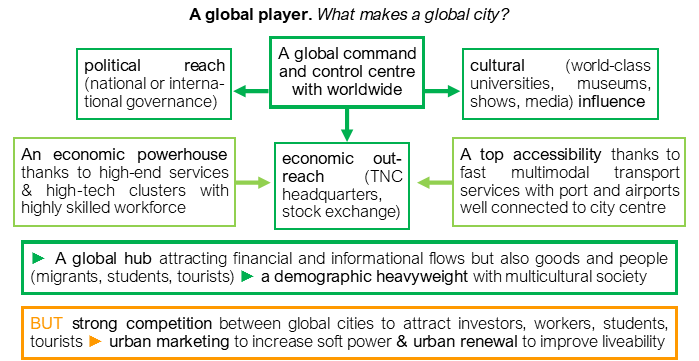
• global city: powerful command and control centre with a worldwide political, economic and cultural influence/reach/outreach.
• globalisation current stage: digital and financial globalisation boosting high-end IT, financial & business services. (+2E-G &1E-H def)
• Brexit: UK’s decision to leave the EU based on the June 2016 referendum and effective in January 2021. The UK voted to leave by 51.9% but London voted to remain by 59.9%.
Connectivity
• hub: a focal network node attracting inflows and producing outflows.
• accessibility: fast, multimodal transport services to facilitate trade and mobility.
• mobility: move from one’s home to a new location. Called migration if it’s to settle permanently or temporarily (migrants). Called commuting: when it’s a daily trip from home to one’s workplace (commuters).
Urban production space
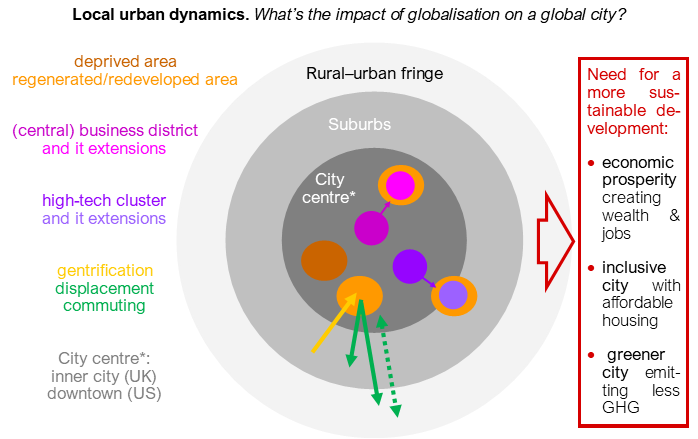
• business district (UK) / central business district (US): central urban hub concentrating high value-added financial and commercial activities. The newest have a specific skyline (skyscrapers).
• cluster: concentration of interconnected high-tech/creative/digital businesses and associated education/research institutions.
• TNC, MNC: trans/multinational corporation/company operating internationally.
• GAFAM, Big Five or Big Tech: Google, Apple, Facebook, Amazon & Microsoft, the top 5 IT corporations.
• digital or I(C)T: information (& communication) technology.
Urban policy and trend
• urban marketing: promoting a positive image using advertising to increase soft power: the ability to influence using attraction rather than force or coercion.
• urban renewal or regeneration (UK)/redevelopment (US): build or renovate housing, workspaces, leisure & transport facilities etc... to improve and densify an area.
• urban sprawl: the spreading of suburban developments (such as houses and shopping centres) on undeveloped land in the (rural) urban fringe.
Urban challenges
• liveability: quality of life, day-to-day living conditions including housing, health-care, education, culture, environment and transport.
• deprivation: economic poverty (income, jobs), social inequality (education, health, housing) and environmental dereliction (degraded cityscape).
• gentrification: higher income groups moving to attractive areas and displacing lower income groups. Called super-gentrification if involving the global super-rich investing in a city.
• polarised city: city fragmented into exclusive neighbourhoods based on income and/or ethnicity. The opposite of an inclusive city.
• congestion: a situation in which a place is too blocked (road) or crowded (city-centre, public transport), causing difficulties.
2E notions
Developed/developing/emerging country, sustainable/unsustainable development, push/pull factor, multicultural society, climate change, economic transition to knowledge-based services (diagram), energy/tourist transition. “Political” buildings.